※ 우선순위 큐 (Priority Queue)
우선순위 개념을 큐에 대입한 자료구조로 컴퓨터 분야에서 다양하게 이용된다.
우선순위 큐는 다양한 방법(배열, 연결리스트, ...)으로 구현할 수 있지만 가장 효율적인 구조는 힙(Heap)이다.
이런 우선순위 큐는 어떤 요소가 먼저 삭제될 것인지에 따라 다음 2가지로 나뉜다.
최대 우선순위 큐: 우선순위가 가장 높은 것 먼저 삭제
최소 우선순위 큐: 우선순위가 가장 낮은 것 먼저 삭제
※ 힙 (Heap)
힙 (heap)은 완전 이진트리(complete binary tree)의 일종으로 우선순위 큐를 위해 만들어진 자료구조다.
힙(heap)은 요소들이 완전히 정렬된 것은 아니지만 일종의 반 정렬상태를 유지한다.
이로 인해 삽입 삭제의 시간복잡도가 O(log n)으로 다른 방법보다 훨씬 유리하다.
이런 힙은 여러 개의 값들 중 최댓값과 최솟값을 빠르게 찾아내기 위해 만들어진 자료구조이다.
이를 위해 부모 노드의 key 값 > 자식 노드의 key 값 을 항상 만족하도록 만들어졌다. (보통 최대힙으로 가정하는 편)
단, BST와는 다르게 Heap tree는 중복된 값을 허용한다.
- 최대 힙 (max heap)
key(부모) ≥ key(자식)

- 최소 힙 (min heap)
key(부모) ≤ key(자식)
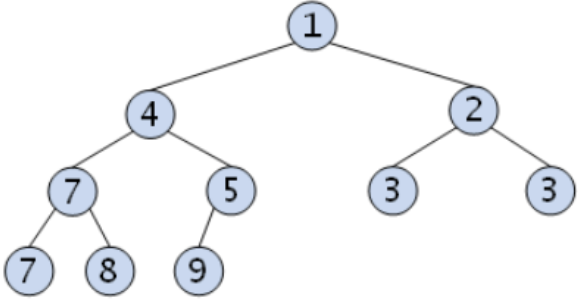
✯ 힙의 기본 틀
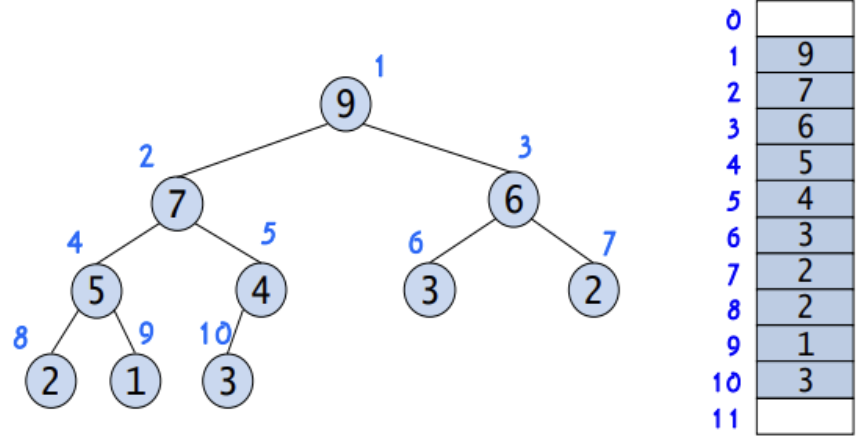
왼쪽 자식의 index = 부모 index * 2
오른쪽 자식의 index = 부모 index* 2 + 1
∴ 부모의 index = 자식의 index / 2
※ MaxHeap의 삽입연산 (insert)
힙에 새로운 요소가 들어오면
1. 힙의 마지막 노드에 이어서 새 노드를 삽입
2. 삽입 후 새 노드를 부모노드와 교환하여 힙의 성질을 만족시켜준다.
✯ BST의 insert Algorithm
insert (key)
heapSize <- heapSize + 1;
i <- heapSize;
node[i] <- key;
while i != 1 and node[i] > node[PARENT(i)] do
node[i] ↔ node[PARENT(i)]; // 노드를 서로 교환
i <- PARENT(i);
※ MaxHeap의 삭제연산 (delete)
1. 먼저 root노드 삭제 후, 빈 루트에 힙의 마지막 노드를 가져 온다. (레벨순회 순 마지막 노드)
2. 순차적으로 강등 진행 (자식들 중 더 큰 값과 교환 진행)
✯ BST의 delete Algorithm
remove()
item <- A[1];
A[1] <- A[HeapSize];
i <- 2;
while i ≤ heapSize do
if i <heapSize nad A[LEFT(i)] > A[RIGHT(i)]
then largest <- LEFT(i);
else largest <- RIGHT(i);
if A[PARENT(largest)] > A[largest]
then break;
A[PARENT(largest)] ↔ A[largest];
i <- LEFT(largest);
return item;
※ MaxHeap 구현
- HeapNode.h
#include <iostream>
#define MAX_ELEMENT 200 // heap array size
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class Node{
private:
int key;
T data;
public:
Node(){ key = 0; }
Node(int key, T _data){
this->key = key;
this->data = data;
}
~Node(){}
// getter/setter
int getKey(){ return key; }
void setKey(int key){ this->key = key; }
T getData(){ return data; }
void setData(T data){ this->data = data; }
};
template <typename T>
class MaxHeap{
private:
Node<T> node[MAX_ELEMENT];
int size; // heap 요소 개수
public:
MaxHeap(){ size = 0; }
~MaxHeap(){}
// search node
Node<T>& getParent(int index){
return node[index/2];
}
Node<T>& getLeftChild(int index){
return node[index*2];
}
Node<T>& getRightChild(int index){
return node[index*2+1];
}
// 삽입
void insert(int key, T data){
if(isFull()){
cout << "Heap is Full" << endl;
return;
}
int index = ++size; // 힙트리 마지막 노드의 다음 위치에서 시작
// 힙트리를 거슬러 올라가며 부모 노드와 비교
while(index != 1 && key > getParent(index).getKey()){
node[index] = getParent(index);
index /= 2;
}
// 최종 위치에 데이터 삽입
node[index].setKey(key);
node[index].setData(data);
}
// 삭제
T remove(){
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "Heap is Empty" << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
Node<T> itemNode = node[1]; // root node (삭제 대상)
Node<T> lastNode = node[size--]; // 힙트리의 마지막 노드
int index = 1; // 마지막 노드의 index (root 부터 시작)
// root 부터 내려가며 자식 노드와 비교
while(index <= size){
if(index*2 > size){ // leaf node인 경우 (자식 노드가 없는 경우)
break;
}
else if(index*2 == size){ // 자식노드가 하나인 경우
if(lastNode.getKey() < getLeftChild(index).getKey()) {
node[index] = getLeftChild(index);
index *= 2;
}
else
break;
}
else{ // 자식노드가 두개인 경우
int leftChildKey = getLeftChild(index).getKey();
int rightChildKey = getRightChild(index).getKey();
// 둘 중 key가 더 큰 자식노드와 교환
if(lastNode.getKey() < leftChildKey || lastNode.getKey() < rightChildKey){
node[index] = leftChildKey > rightChildKey ? getLeftChild(index) : getRightChild(index);
index = leftChildKey > rightChildKey ? index*2 : index*2+1;
}
else
break;
}
}
node[index] = lastNode; // 마지막 노드를 최종 위치에 저장
return itemNode.getData(); // 삭제 노드의 data 반환
}
// 출력
void display(){
int level = 1;
for(int i=1; i<= size; i++){
if(i == level){
cout << endl;
level *= 2;
}
cout << node[i].getData() << "(" << node[i].getKey() << ") ";
}
cout << '\n' << "-------------------------" << endl;
}
bool isEmpty(){ return size == 0; }
bool isFull(){ return size == MAX_ELEMENT - 1; }
};- main.cpp
#include "HeapNode.h"
int main(){
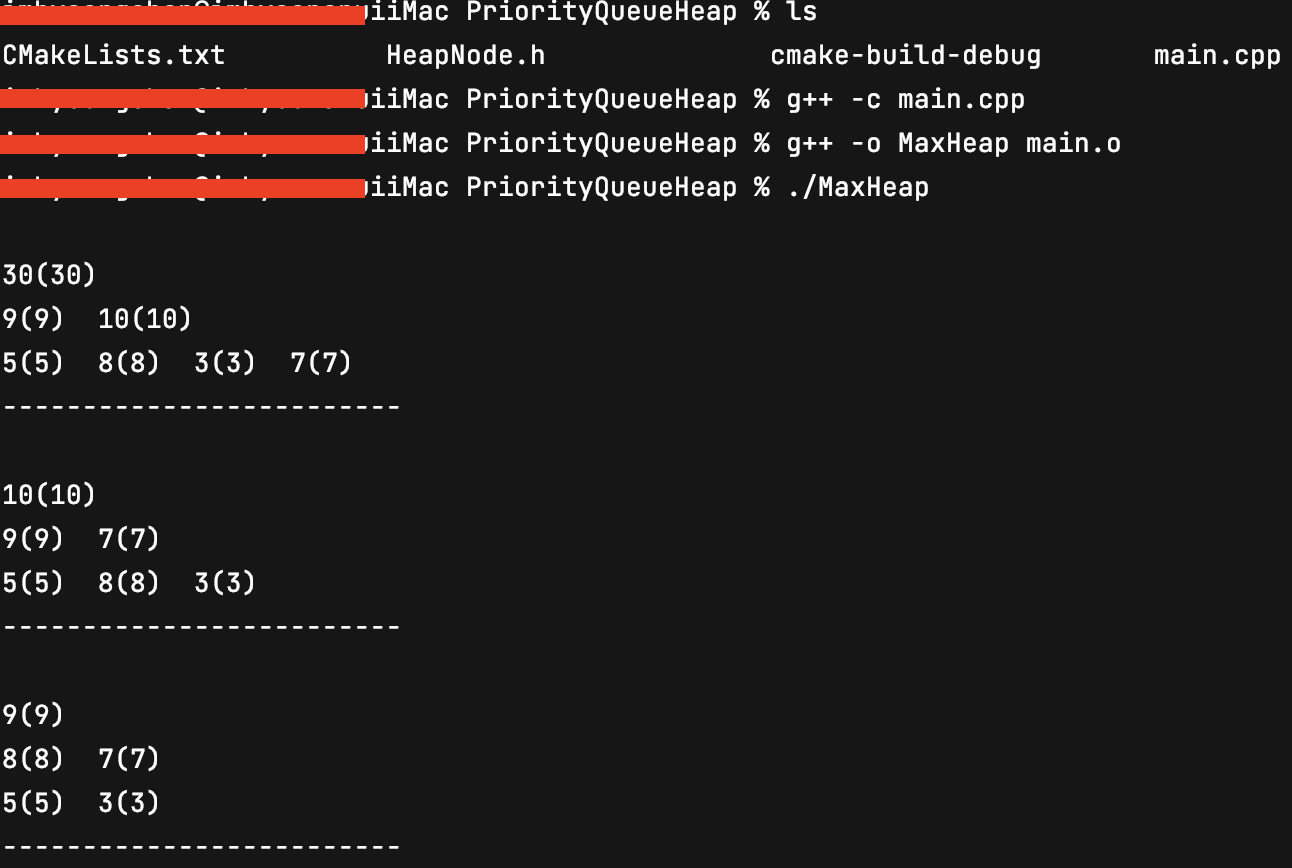
MaxHeap<int> priorityQueue;
// 삽입
priorityQueue.insert(10, 10);
priorityQueue.insert(5, 5);
priorityQueue.insert(30, 30);
priorityQueue.insert(8, 8);
priorityQueue.insert(9, 9);
priorityQueue.insert(3, 3);
priorityQueue.insert(7, 7);
priorityQueue.display();
// 삭제
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.display();
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.display();
return 0;
}
'C | C++ > Data Structure & STL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| this.code(10).DS_ sort II. [insertion, selection, bubble]sort (0) | 2023.01.03 |
|---|---|
| this.code(9).DS_ sort I. [heap, merge, quick]sort (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| this.code(7).DS_ BST (Binary Search Tree). & AVL tree (0) | 2023.01.02 |
| this.code(6).DS_ Tree, Binary Tree (0) | 2023.01.02 |
| this.code(5).DS_ List (4) | 2022.12.23 |