※ 선형 자료구조
앞서 우리가 배운 것들은 모두 선형 자료구조에 속하는데 대표적으로 다음과 같다.
- stack, queue, deque, list . . .
이와 달리 선형이 아닌 "계층적 구조 (hierarchical)"를 표현하기 위해 사용되는 자료구조인 트리(tree)에 대해 알아보고자 한다.
컴퓨터 저장장치의 디렉토리 구조도 계층적인 자료구조로 많은 상황에서 사용되기에 자료구조를 배우는 이유중 하나라 할 수 있다.
자료구조의 양대산맥이라 생각될 정도로 그래프만큼 많이 사용되며 자주 사용되는 자료구조이기에 잘 익혀두자!
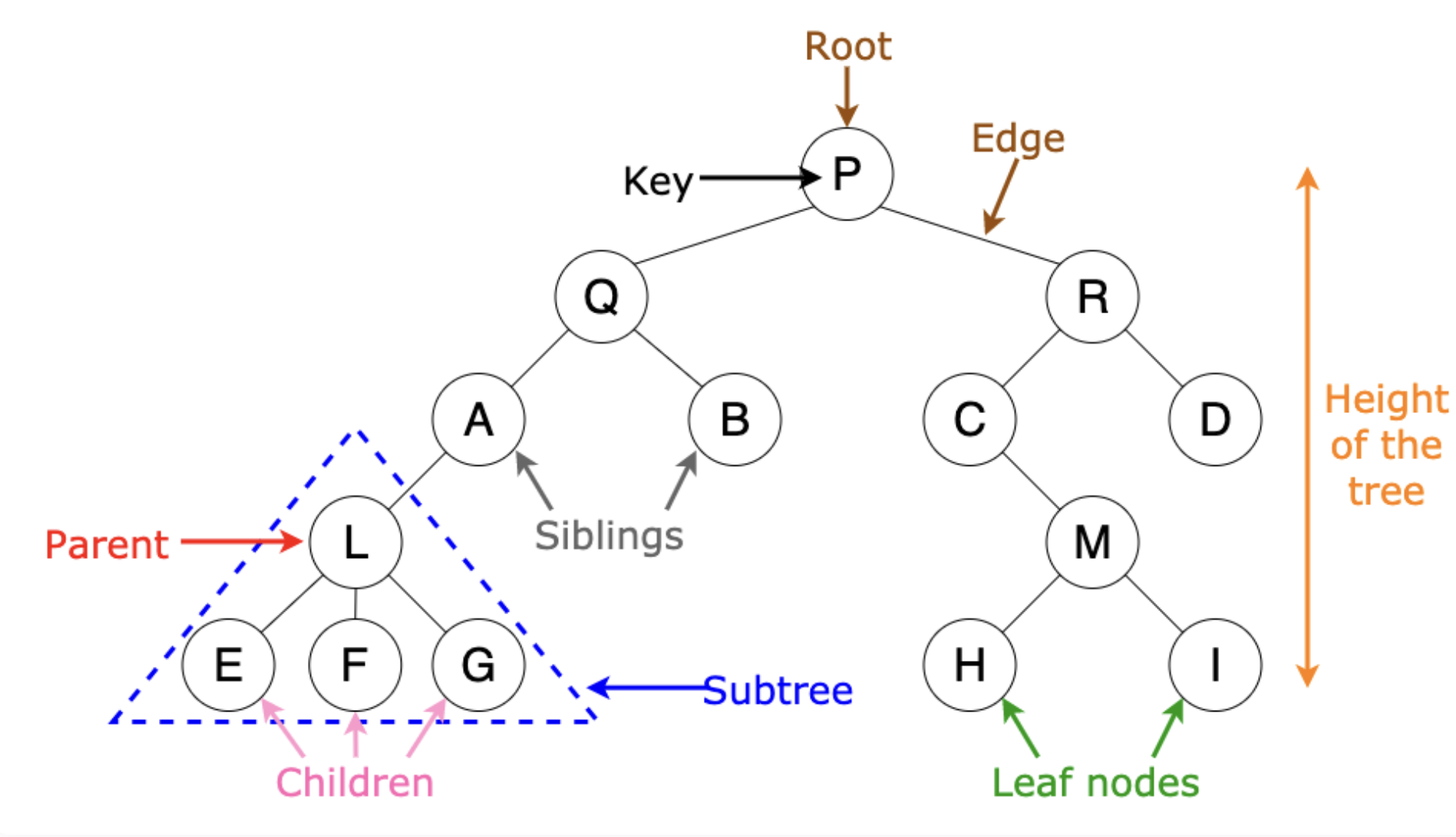
※ 트리 용어
트리의 구성요소로는 루트(root), 서브트리(subtree), 간선(edge), 노드(node) 등이 있다.
- 차수(degree): 어떤 node가 갖는 자식노드의 개수
- 레벨(level): 트리의 층 수로 root를 level 0이나 1로 매긴다.(책마다 조금씩 다름)
- 높이(height): 트리의 각 층에 번호를 매기는 것으로 트리의 높이는 최대 레벨을 통해 결정할 수 있다.
※ 이진트리 (Binary Tree)
모든 노드의 차수가 2 이하이며 왼쪽 서브트리와 오른쪽 서브트리가 반드시 구별되어야 한다.
n개의 노드는 n-1개의 간선(edge)를 가지며 높이가 h인 이진트리의 최대 노드 개수는 2^h - 1이다.
n개의 노드를 갖는 이진트리의 높이는 다음과 같다. ⎡log(n+1)⎤ ≤ h ≤ n
포화이진트리(full binary tree): 모든 레벨의 노드가 꽉 차있는 트리, 높이가 h라면 총 2^h-1개의 노드를 갖는다.
완전이진트리(complete binary tree): 레벨 1~h-1까지는 모두 노드가 채워져 있고 마지막 레벨 h는 왼쪽~>오른쪽으로 순서대로 채워진 트리이다. (즉, 마지막 레벨의 노드가 꽉 차있지 않아도 됨)
대표적인 완전이진트리 예로는 힙(heap)이 있다.
※ 이진트리 순회 알고리즘
✯ 전위 순회 (preorder)
preorder(x)
if x != null
then print data(x); // 루트(x)노드 처리
preorder(LEFT(x)); // 왼쪽 subtree 방문
preorder(RIGHT(x)); // 오른쪽 subtree 방문
✯ 중위 순회 (inorder)
inorder(x)
if x != null
then inorder(LEFT(x)); // 왼쪽 subtree 방문
print data(x); // 루트(x)노드 처리
inorder(RIGHT(x)); // 오른쪽 subtree 방문
✯ 후위 순회 (postorder)
postorder(x)
if x != null
then postorder(LEFT(x)); // 왼쪽 subtree 방문
postorder(RIGHT(x)); // 오른쪽 subtree 방문
print data(x); // 루트(x)노드 처리
※ 이진트리 노드 개수 및 높이 구하는 알고리즘
✯ node 개수 구하기
getCount(x)
if x == null
then return 0;
else return 1 + getCount(LEFT(x)) + getCount(RIGHT(x));
✯ leaf node 개수 구하기
getLeafCount(x)
if x == null
then return 0;
if LEFT(x) == null and RIGHT(x) == null
then return 1;
else return getLeafCount(LEFT(x)) + getLeafCount(RIGHT(x));
✯ height 구하기
getHeight(x)
if x == null
then return 0;
else return 1 + max(getHeight(LEFT(x)), getHeight(RIGHT(x)));
※ 이진트리 구현
✯ BinaryNode.h
#include <iostream>
class BinaryNode{
protected:
int data;
BinaryNode* left;
BinaryNode* right;
public:
BinaryNode(int val = 0, BinaryNode *l = nullptr, BinaryNode *r = nullptr) : data(val), left(l), right(r) { }
void setData(int val) { data = val; }
void setLeft(BinaryNode* l) { left = l; }
void setRight(BinaryNode* r) { right = r; }
int getData() const { return data; }
BinaryNode* getLeft() const { return left; }
BinaryNode* getRight() const { return right; }
bool isLeaf() const { return left == nullptr && right == nullptr; }
};
✯ BinaryTree.h
#include "BinaryNode.h"
using namespace std;
class BinaryTree {
private:
BinaryNode *root;
public:
BinaryTree() : root(nullptr) { };
void setRoot(BinaryNode * node) { root = node; }
BinaryNode * getRoot() { return root; }
bool isEmpty() { return root == nullptr; }
// 이진트리의 순회연산 (전위, 중위, 후위, 레벨 순회)
void inorder() { cout << endl << "inorder: "; inorder(root); }
void inorder(BinaryNode *node) {
if (node != nullptr) {
inorder(node->getLeft());
cout << node->getData() << " ";
inorder(node->getRight());
}
}
void preorder() { cout << endl << "preorder: "; preorder(root); }
void preorder(BinaryNode *node) {
if (node!= nullptr) {
cout << node->getData() << " ";
preorder(node->getLeft());
preorder(node->getRight());
}
}
void postorder() { cout << endl << "postorder: "; postorder(root); }
void postorder(BinaryNode *node) {
if (node!= nullptr) {
postorder(node->getLeft());
postorder(node->getRight());
cout << node->getData() << " ";
}
}
// 이진트리의 추가 연산 (이진트리 노드의 개수 구하기 ,단말노드개수 구하기, 높이 구하기)
int getCount() { return isEmpty() ? 0 : getCount(root); }
int getCount(BinaryNode *node) {
if (node == nullptr) return 0;
return 1 + getCount(node->getLeft()) + getCount(node->getRight());
}
int getLeafCount() { return isEmpty() ? 0 : getLeafCount(root); }
int getLeafCount(BinaryNode *node) {
if (node == nullptr) return 0;
if (node->getLeft()) return 1;
else
return getLeafCount(node->getLeft()) + getLeafCount(node->getRight());
}
int getHeight() { return isEmpty() ? 0 : getHeight(root); }
int getHeight(BinaryNode *node) {
if (node == nullptr) return 0;
int hLeft = getHeight(node->getLeft());
int hRight = getHeight(node->getRight());
return (hLeft > hRight) ? hLeft + 1 : hRight + 1;
}
};
✯ main.cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
BinaryTree tree;
BinaryNode *d = new BinaryNode('D', nullptr, nullptr);
BinaryNode *e = new BinaryNode('E', nullptr, nullptr);
BinaryNode *b = new BinaryNode('B', d, e);
BinaryNode *f = new BinaryNode('F', nullptr, nullptr);
BinaryNode *c = new BinaryNode('C', f, nullptr);
BinaryNode *a = new BinaryNode('A', b, c);
tree.setRoot(a);
tree.inorder();
tree.preorder();
tree.postorder();
cout << endl;
cout << "노드의 개수 = " << tree.getCount() << endl;
cout << "leaf의 개수 = " << tree.getLeafCount() << endl;
cout << "tree의 높이 = " << tree.getHeight() << endl;
/********************************************************************/
//inorder: 68 66 69 65 70 67
//preorder: 65 66 68 69 67 70
//postorder: 68 69 66 70 67 65
//노드의 개수 = 6
//leaf의 개수 = 1
//tree의 높이 = 3
}
'C | C++ > Data Structure & STL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| this.code(8).DS_ Priority Queue. &. Heap (0) | 2023.01.03 |
|---|---|
| this.code(7).DS_ BST (Binary Search Tree). & AVL tree (0) | 2023.01.02 |
| this.code(5).DS_ List (4) | 2022.12.23 |
| this.code(4).DS_ Recursion (재귀)_최대공약수 (0) | 2022.10.30 |
| ★this.code(3).DS_ Queue & (STL): queue, deque (0) | 2022.10.30 |